
Bazel is a free and open-source build and test tool developed by Google. Bazel uses a declarative language (Starlark) to describe the build and test steps.
This simple guide shows how to use variables in Bazel. This can be simple done in 3 steps.
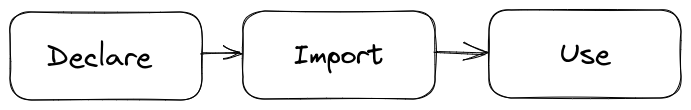
We’ll use an fictional example of setting Java 17 as the default version of the project to show you how to use variables in Bazel.
1: Define the Variable in a .bzl File
In this example we define the Variable in rules/jdk/compatibility.bzl
1 | JDK17_UPWARDS = select({ |
We use the select function to choose the suitable value for the JDK17_UPWARDS variable based on the current platform. In the example, we use Java 17 upwards if the platform supports it, or an empty list otherwise.
2: Import the Variable in your BUILD File
We use the load function to load specific Bazel file and import the variable from it. So, to do this we just add the line below to the BUILD file:
1 | load("//rules/jdk:compatibility.bzl", "JDK17_UPWARDS") |
It loads the compatibility.bzl file and imports the JDK17_UPWARDS variable.
3: Use the Variable
Just use the variable in your BUILD file:
1 | java_library( |
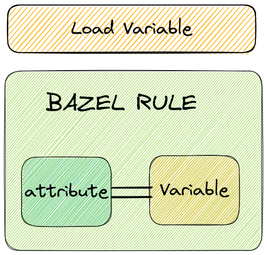
In our example, we use the JDK17_UPWARDS variable in the java_library rule as the attribute named target_compatible_with. This attribute specifies the versions of the Java language that the target is compatible with.
ERROR: name is not defined
You could have the issue below:
1 | ERROR: /builds/platform/nasa/libs/nasa_atlantis-web/BUILD:22:30: name 'JDK17_UPWARDS' is not defined |
The reason is likely because you forgot to import the variable in your BUILD file or the path is wrong. For example you use
1 | load("///rules/jdk:compatibility.bzl", "JDK17_UPWARDS") |
instead of
1 | load("//rules/jdk:compatibility.bzl", "JDK17_UPWARDS") |
Thats it.
Follow me in the group in telegram